Have you ever felt a lump in your breast and immediately feared the worst? You’re not alone. Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, and its mere mention can send shivers down anyone’s spine. But knowledge is power, and understanding this disease is the first step towards beating it.
In this article, we have a comprehensive guide into the world of breast cancer, trying to demystify all its complexities and light upon crucial aspects that each woman-and man-ought to know. Starting from early warning signs up to the latest treatment options available, we will make you ready to face the fight against this formidable foe head-on.
Come to understand what is breast cancer starting from the very nature itself and on to symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and much more. Whether a survivor, caregiver, or just interested in staying knowledgeable, the journey through six key aspects of breast cancer will empower one with knowledge and hope. Let’s start with understanding what exactly breast cancer is and why it has assumed such paramount importance in our lives.

Understanding Breast Cancer
A. Definition and Elementary Explanation
Breast cancer is a complex disease resulting from the uncontrollable growth and division of cells within breast tissue, which can give rise to a malignant tumor. Abnormal growth can originate from various areas of the breast, such as ducts, lobules, or connective tissue. Even though this disease predominantly afflicts women, it may also affect men though to a much lesser extent.
B. Classification of Breast Cancer
There are four types of breast cancer and each is characteristically different.
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)
- Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer
| DCIS | Non-invasive, confined to milk ducts | 20-25% |
| IDC | Starts in ducts, spreads to surrounding tissue | 70-80% |
| ILC | Begins in milk-producing lobules | 10-15% |
| Triple-Negative | Lacks common receptors, aggressive | 10-20% |
| Inflammatory | Rare, aggressive, affects skin | 1-5% |
C. Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer among women globally, with millions of new cases diagnosed every year. Though anyone can develop breast cancer, there are several factors that increase the risk:
- Age (risk increases with age)
- Family history of breast cancer
- Personal history of breast cancer or some benign breast diseases
- Inherited gene mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2)
- Dense breast tissue
- Early menarche or late menopause.
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Obesity
- Alcohol drinking
- Lack of physical activity
D. Early Detection Importance
Early detection will enhance the chances of effective treatment and survival. Monitoring will be possible at earlier stages when intervention is manageable through regular screening and checking for lumps by an individual. Some benefits through early detection include
- Options of treatment
- Higher prospects of complete cure
- Improved quality of life during and after treatment
- Lesser demand for strong treatments
- Better long-term survival rates
Now that we have a good understanding of breast cancer, including its definition, types, prevalence, and the importance of early detection, we can explore more about cancer’s causes, symptoms, and treatment, before discussing the signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of this disease.
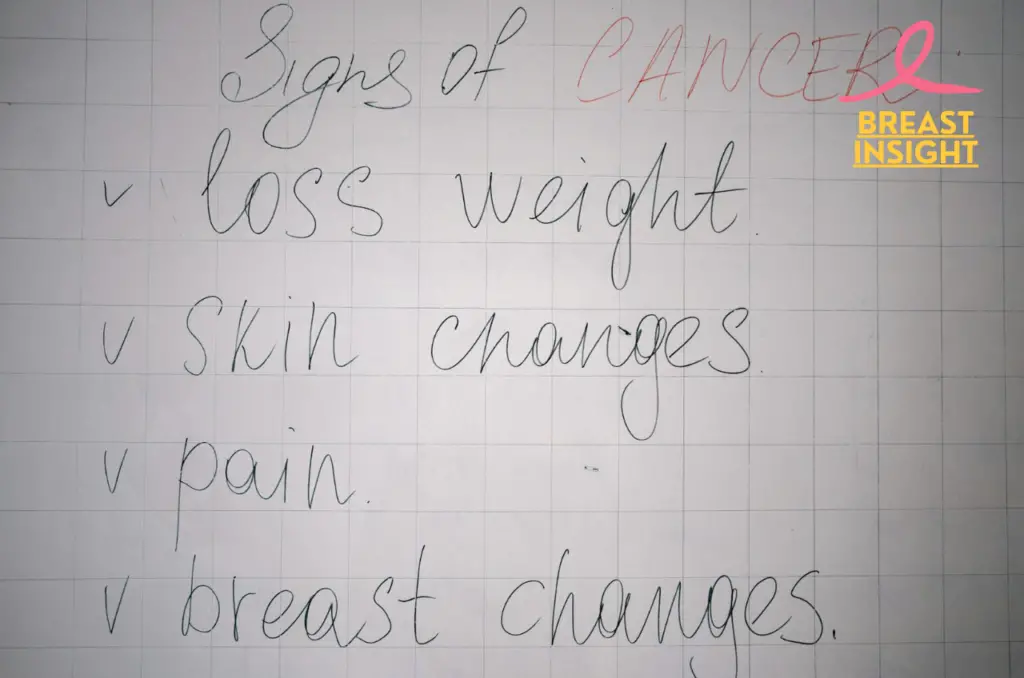
Sign and Symptoms
Since we now roughly understand breast cancer, it will be of utmost importance to know its symptoms. As early detection has increased in relation to treatment, monitoring changes in one’s body is crucial.
General Physical Changes
The most noticeable signs of breast cancer often involve physical changes in the breast or surrounding areas. These may include:
- A new lump or thickening in the breast or underarm area
- Changes in breast size, shape, or appearance
- Indentations, puckers or bulges of the skin
- A change in the direction or inversion of the nipple
- Redness, scaliness, or thickening of the nipple or breast skin
It’s important to note that not all lumps are cancerous, but any new or unusual changes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
| Change | Description | Action |
| Lump | A hard, painless mass in the breast or underarm | Consult doctor immediately |
| Skin changes | Dimpling, puckering, or orange-peel texture | Schedule a check-up |
| Nipple changes | Inversion, discharge, or direction change | Seek medical evaluation |
While breast cancer is not always painful, some people report discomfort or other symptoms. These can include:
- Continued breast pain or tenderness
- Unprovoked swelling in the breast
- Warm or hot sensation in the involved area
- Breast or nipple itching or tenderness
Keep in mind that breast pains are mostly connected to hormonal alteration or noncancerous conditions, though if your pain has developed recently and is continuing on, perhaps along with some other associated symptoms, do consult the doctor.
Less Common Symptoms to Monitor:
Some other less common but just as critical signs of breast cancer include:
- Swelling in the armpit or collarbone region
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic coughing or hoarseness
Such symptoms may be an indication that the cancer has spread beyond the tissue of the breast. They may be caused by other conditions, but it is a good idea to have them checked, especially if they are persistent or worsening.
Let’s proceed with noting the fact that one doesn’t have breast cancer for sure if getting one or more of those symptoms. However, then be watchful about any change to your body and take medicine as early as possible while noticing something odd to this body of yours, whereby early detection and proper remedy are done. Now let us proceed with the diagnosis steps of breast cancer through one of the methods listed above to give you a wide experience of how diagnosis takes place.

Diagnosis Techniques
That, we have now discussed above symptoms of breast cancer. Moving ahead, we will know different diagnostic techniques for such disease. Early and appropriate diagnosis is essential for adequate treatment and better prognosis.
A. Mammograms and their role
The tools used mostly for the screening and diagnosis of breast cancer are mammograms. They allow the detection of abnormality before it is felt. Mammography comes in two broad categories.
- Screening mammograms Annual studies on asymptomatic women
- Diagnostic mammograms High-resolution images to investigate a suspicious area.
Mammograms can detect
- Masses or lumps
- Calcifications
- Structural distortions
| Mammogram Type | Purpose | Frequency |
| Screening | Early detection | Annually or biennially |
| Diagnostic | Investigate abnormalities | As needed |
B. Ultrasound and MRI scans
In cases where mammograms are inconclusive or additional information is needed, doctors may suggest:
Ultrasound
- Uses sound waves to generate images
- Helps differentiate between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts
- Most useful for females with dense breast tissue
MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Works through magnetic fields and radio waves
- Provides detailed cross-sectional images of breast tissue
- Always used in high-risk patients or in assessment of known cancers.
C. Biopsy Procedures
The gold standard of diagnosing breast cancer is through a biopsy. This is the removal of a small amount of breast tissue for laboratory examination. Common types of biopsy include:
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA)
- Core needle biopsy
- Stereotactic biopsy
- Surgical biopsy
This choice of biopsy would depend on such factors as
- Dimensions and place of the suspicious region
- Patient’s overall health
- Physician’s preference
D. Genetic testing options
Genetic testing can be done for the evaluation of risk and selection of treatment. The indications are:
- Patients with a positive family history of breast cancer.
- Those diagnosed in early childhood
- Select patients with types of breast cancer
Common genes tested include:
- •BRCA1 and BRCA2
- TP53 (linked to Li-Fraumeni syndrome)
- PTEN (associated with Cowden syndrome)
| Test Type | Purpose | Candidates |
| Germline testing | Identify inherited mutations | High-risk individuals |
| Tumor genomic profiling | Guide treatment decisions | Diagnosed patients |
The testing does involve genetic counseling which is to help patients understand the implications of such results.
As we move forward, the various treatment options for individuals diagnosed with breast cancer would be discussed, taking from the knowledge gained through the diagnostic methods.

Treatment Options
Now that we have gone through how breast cancer is diagnosed, let’s take a look at the treatments available to patients. Depending on the type and stage of breast cancer, and also the patient’s overall health and personal preferences, there are several treatment options for breast cancer.
A. Surgery: Lumpectomy vs. Mastectomy
Surgery is often the primary treatment for breast cancer. The two main surgical options are:
- Lumpectomy: A breast-conserving surgery where only the tumor and some surrounding tissue are removed.
- Mastectomy: Removal of the whole breast.
Here’s a comparison of these two surgical approaches:
| Aspect | Lumpectomy | Mastectomy |
| Tissue removal | Only tumor and surrounding area | Entire breast |
| Recovery time | Generally shorter | Usually longer |
| Radiation therapy | Typically required after surgery | May not be necessary |
| Cosmetic outcome | Preserves most of the breast | More significant change in appearance |
| Recurrence risk | Slightly higher | Slightly lower |
B. Radiation Therapy Advantage
Radiation therapy employs high energy beams to destroy cancer cells. Its benefits include:
- Decrease the risk of cancer coming back
- Targeting remaining cancer cells after surgery
- Tumor downsizing before surgery
- Symptom Management in palliative stages
C. Chemotherapy Strategies
Chemotherapy utilizes drugs in an effort to eradicate cancer cells in the body. There are several types.
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Given before surgery to shrink tumors
- Adjuvant chemotherapy: Given after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells
- Palliative chemotherapy: To control symptoms during advanced stages
D. Hormone Therapy Effectiveness
Hormone therapy is effective in hormone receptor-positive breast cancers. It acts by
- Blocking hormone synthesis
- Prevent hormones from binding to cancer cells.
- Reduces the risk of recurrence to up to 50%.
E. Targeted Drug Therapies
Targeted therapies target specific characteristics of cancer cells. Examples include:
- HER2-targeted drugs (e.g., trastuzumab)
- CDK4/6 inhibitors
- PARP inhibitors
These have fewer side effects than the normal chemotherapy and are quite effective for some types of breast cancers.
Understanding these alternatives for treatment, the patient can collaborate with their healthcare team to create a plan of treatment that will meet his or her needs. Treatment will depend on the level of cancer, as well as the patient’s health considerations and what is in their best interest. In the future, we will discuss life with breast cancer and how patients can manage daily living throughout treatment and after diagnosis.
Living with Breast Cancer
Now that we have discussed the treatments, let’s talk about the difficulties and strategies in managing breast cancer.
Coping Strategies with Patients
Living with breast cancer is emotionally as well as physically exhausting. Some of the very effective coping strategies are:
- Educate yourself: Knowledge is power. Understanding your condition can help you feel more in control.
- Express your emotions: Do not bottle up the emotions. Share it with trusted friends, family members, or a therapist.
- Practice mindfulness. Meditation, for instance, reduces stress and anxiety.
- Set feasible goals: Break broad goals into manageable steps to avoid being overwhelmed.
- Routine: Stick to a daily routine that would help provide structure and normalcy.
- Support Systems and Resources
Support Systems and Resources
A strong support network is crucial for breast cancer patients. The following are useful resources:
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences can be incredibly beneficial.
- Online Communities: Sites like breastcancer.org allow patients to connect and exchange advice through forums.
- Professional Counseling: Mental health specialists provide a professional counseling setting.
- Treatment Financial aid programs: Organizations providing treatment and all the costs that go with it offer their patients financial assistance.
| Resource Type | Examples | Benefits |
| Support Groups | Local hospital groups, Breast Cancer Support Community | Emotional support, shared experiences |
| Online Communities | breastcancer.org, Cancer Survivors Network | 24/7 access, diverse perspectives |
| Professional Counseling | Oncology social workers, psychologists | Specialized mental health support |
| Financial Assistance | Susan G. Komen Foundation, CancerCare | Help with medical bills, transportation costs |
Life style interventions for better result
Some lifestyle modifications improve the quality of life and could optimize treatment outcomes:
- Balanced Diet .Consume mostly nutrient-rich foods, such as fruits and vegetables and whole grains, limit processed and alcoholic beverages.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity, even gentle exercises like walking or yoga, can boost energy levels and mood.
- Sleep, which is getting 7 to 9 hours a day, for effective health and full recovery.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate relaxation through deep breath exercise or journaling as part of one’s regular daily routine.
- Alternative Therapy: Talk to your healthcare professional about the use of alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage.
Living with breast cancer is, of course difficult, but with the proper strategies, support, and lifestyle changes, many patients learn how to live good-quality lives. Remember, each patient’s journey is different, and it is really important to work closely with your healthcare team to find a way to live your life well with breast cancer.
As we proceed, we will discuss prevention and risk-reducing interventions to decrease the occurrence of breast cancer, one of the most important aspects for patients and the broader community.

Prevention and Risk Reduction
There is no surefire way to prevent breast cancer, but there are several strategies to reduce your risk and detect it early. Let’s look at these important approaches:
Routine Tests
Regular screenings are important in detecting breast cancer early. The following is a general outline of recommended screening methods:
| Screening Method | Recommended Frequency | Age Group |
| Mammogram | Every 1-2 years | Women 40+ |
| Clinical Breast Exam | Annually | Women 40+ |
| Breast Self-Exam | Monthly | All Women |
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle significantly reduces the risk of getting breast cancer. The factors are as follows:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly at least 150 minutes of moderate activity per week.
- Reduce alcohol intake
- Quit smoking
- Follow a balanced, nutritious diet rich in fruits and vegetables
Genetic Test
For those whose family history includes breast cancer, genetic testing can be the most important source of information related to your risk. Genetic testing may include testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations. These are associated with higher risks of breast cancer.
Preventive medications
Doctors may sometimes recommend preventive drugs, or chemoprevention. The drugs lower the risk of breast cancer in people at high risk. These may include:
- Tamoxifen
- Raloxifene
- Aromatase inhibitors
By implementing these prevention and risk reduction strategies, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining breast health and possibly reducing your risk of breast cancer.
Conclusion
Breast cancer is an unscrupulous and serious disease that affects millions of women worldwide. Starting with understanding its nature through different methods of detection, treating the disease, and strategies on how to live with it as well, and knowledge indeed seems to be power in a fight against breast cancer. Improvement in outcomes would involve early detection through periodic scanning and self-examinations while new treatments provide hopeful news for those afflicted. The risk reduction and prevention strategies are important while advances in treatment continue to offer hope for those diagnosed. A healthy lifestyle, knowledge of one’s family history, and awareness of the latest research can all contribute to reducing the impact of breast cancer. Support and education are key elements that empower individuals and communities in facing breast cancer with strength and hope.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the early signs of breast cancer?
Most people would ask about the early symptoms of breast cancer so that detection would be done on time. Common symptoms include lumps in the breast or armpit, change in the shape or size of the breast, redness or puckering of the skin, and abnormal discharge from the nipple. Consult your health care provider at once if you see these symptoms.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
Breast cancer diagnosis is usually a multi-modality process that may involve mammograms, ultrasounds, MRIs, and biopsies. In routine screening, usually, mammograms are taken first, and then if there are abnormalities, there is additional imaging or biopsy. Knowing the process helps alleviate fears and encourages one to be proactive about their health.
What are the treatment options for breast cancer?
The treatment for breast cancer varies depending on the stage and type of the condition. The common treatments comprise surgical procedures, such as mastectomy or lumpectomy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. For that reason, it becomes vital to have a consult with your health care professional over the best treatment strategy that should be adopted while addressing the condition.
What is the survival rate for breast cancer?
The survival rate of each type and stage differs, though the five-year survival rate for localized breast cancer is about 99%. Early detection through routine screening and familiarity with symptoms would greatly improve the chances for successful treatment. Understanding the statistics could provide hope to those faced with a breast cancer diagnosis.

22 thoughts on “What is Breast Cancer? Everything You Need to Know”